23 Nov Skin Rejuvenation and Resurfacing
The skin is the largest organ in our bodies. It functions as a barrier to protect our bodies from the outside world and to keep the body hydrated. Over time the quality and texture of our skin begins to decline due to normal age related changes, UV radiation/sun exposure, gravity, and genetic factors. These changes manifest most commonly as laxity of the skin, discoloration/pigmented spots, the appearance of fine blood vessels, and lines/wrinkles. Many treatments exist to address these skin changes including laser resurfacing, chemical peels, microdermabrasion, micro-needling, and intense pulsed light therapy. These treatments work by encouraging changes in various layers of the skin to increase a youthful and healthy appearance. On the face these treatments are primarily used to smooth lines/wrinkles, treat pigmentary changes, even out skin texture, improve scars, and generally volumize and treat aged and/or sun damaged skin. It is helpful to have a basic understanding of skin anatomy to understand these changes and treatment options.
Skin Structure/Function
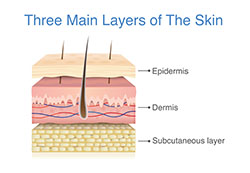
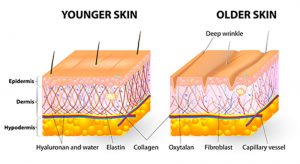
The skin has two primary layers, a superficial layer called the epidermis, and a deeper layer called the dermis. Aging of the skin affects both layers to variable degrees. The epidermis may undergo undesirable textural and pigmentary changes. The dermis contains various proteins including collagen, elastin, and hyaluronic acid that are critical to a tight and youthful skin appearance. These structural elements contained in the dermis are also lost over time. The different treatment modalities for skin rejuvenation all work by re-vitalizing these skin layers and proteins to various degrees. The more aggressive techniques, also known as ablative treatments, penetrate deeper into the dermis and intentionally damage the skin to promote the growth of newer and healthier layers. Less aggressive techniques, known as non-ablative treatments, do not intentionally damage the skin and instead use subtler techniques to slowly encourage skin change.
Ablative Treatments
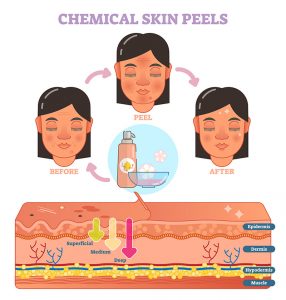
Ablative rejuvenation techniques include laser resurfacing with a carbon dioxide laser, medium or deep chemical peels, or mechanical removal of skin layers known as dermabrasion. Laser resurfacing works by using thermal and light energy to damage the skin at a controlled depth to encourage new skin development. Chemical peels work similarly by using acidic compounds to exfoliate the outer skin layers, whereas dermabrasion involves mechanical removal of the outer layers of the skin using a specialized brush. These treatments take approximately an hour to complete, and usually require the aid of local or topical anesthetics, and/or intravenous sedation. Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages, while all penetrate into the dermis to allow for a more dramatic and long lasting result than non-ablative treatments. While considered the gold standard for optimal skin rejuvenation, these treatments may involve prolonged recovery.
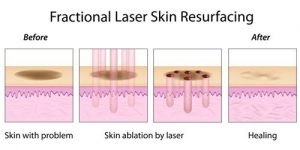
Non-Ablative Treatments
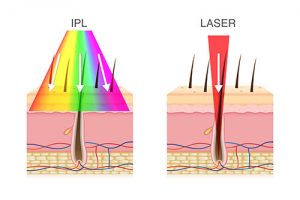
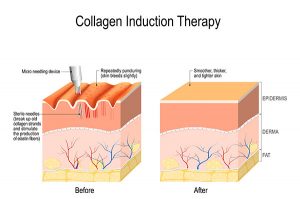
Non-ablative skin resurfacing techniques include light chemical peels, intense pulsed light (IPL), micro-needing, or specialized non-ablative lasers. These techniques are less aggressive than ablative treatments, with minimal recovery time and typically require serial treatments to see and maintain the results. Each of these therapies lasts approximately 30 minutes and requires multiple treatments over the course of several weeks or months, and may require annual maintenance treatments. Light chemical peels work by causing very superficial skin exfoliation and regeneration. IPL uses pulsed light to treat sun damaged areas, pigmented spots, unwanted hair, and fine blood vessels on the face. Non ablative lasers are used to deliver thermal energy that stimulates collagen formation and improves skin structure. Micro-needling uses small needles to create channels in the skin which stimulate collagen production and allow for the better absorption of skin care products and co-treatment with platelet rich plasma (PRP). The main advantage of these treatments is slow and steady skin improvement with rapid recovery between treatments. The main disadvantage is the need for multiple treatments, and less dramatic improvement than with ablative procedures.
Risks and complications
Dr. Chahal will help you determine which of these various techniques will be most beneficial given your specific situation. In general, the ablative techniques involve a longer recovery time and have a higher risk of complication compared to non-ablative techniques. Risks of any skin rejuvenation procedure include pigmentary changes, infection, bleeding, swelling, scarring, or prolonged redness of the treated skin. Please let Dr. Chahal or his staff know if you have a history of cold sores, have previously taken Accutane (Isotretinoin), or have a history of excessive scarring or keloid formation, as this may impact your treatment options. Additionally, ablative techniques are used cautiously in patients with darker skin complexions given an increased risk of post-treatment pigmentary changes. Routine skin care and the use of sunscreens is especially important after any rejuvenation procedure to facilitate the healing process.

